
Learn how to upgrade from Fedora 35 to Fedora 36 with our comprehensive step-by-step guide. Ensure a smooth transition with tips on preparing your system,

Learn how to upgrade from Fedora 35 to Fedora 37 with this comprehensive guide. Follow step-by-step instructions, including preparation, upgrading, and post-upgrade tasks, to ensure a smooth transition. Enhance your system’s performance and security with the latest Fedora features.
Upgrading your Fedora operating system can seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it becomes a straightforward process. This blog post will walk you through upgrading from Fedora 35 to Fedora 37. We’ll cover everything from preparation to post-upgrade tasks, ensuring a smooth transition. Follow along to enjoy the latest features, improved performance, and enhanced security of Fedora 37.
Fedora 37 offers a plethora of new features and improvements over Fedora 35. These include:
Enhanced performance and stability.
Updated software packages.
Improved security features.
New desktop environment options.
By upgrading, you’ll benefit from these enhancements, keeping your system secure and up-to-date. In case you’re wondering if it’s possible to skip Fedora 36 and upgrade directly to Fedora 37.
Yes. It’s possible to upgrade to Fedora 37 from Fedora 35. According to the Official Fedora Documentation, system upgrades are officially supported and tested over a maximum of two releases (e.g., from 35 to 37 or from 38 to 40). If you need to upgrade across more releases, it is recommended to do so in several smaller steps (read more).
Preparation |
Before starting the upgrade, it’s crucial to prepare your system. This involves backing up your data, updating your current Fedora 35 system, and ensuring you have enough disk space for the new installation.
rsync -av --progress /home/user/ /path/to/backup/
Update Fedora 35 |
Ensure your current system is fully updated. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
Fedora 35 - x86_64 7.8 kB/s | 2.8 kB 00:00
Fedora 35 openh264 (From Cisco) - x86_64 4.1 kB/s | 989 B 00:00
Fedora Modular 35 - x86_64 12 kB/s | 2.8 kB 00:00
Fedora 35 - x86_64 - Updates 11 kB/s | 2.8 kB 00:00
Fedora Modular 35 - x86_64 - Updates 12 kB/s | 2.8 kB 00:00
Dependencies resolved.
Nothing to do.
Complete!
This command updates all installed packages to their latest versions, preparing your system for the upgrade.
Check Disk Space |
Upgrading to Fedora 37 requires sufficient disk space. Check your available space using the df command:
df -h
Ensure you have at least 10 GB of free space to accommodate the new installation.
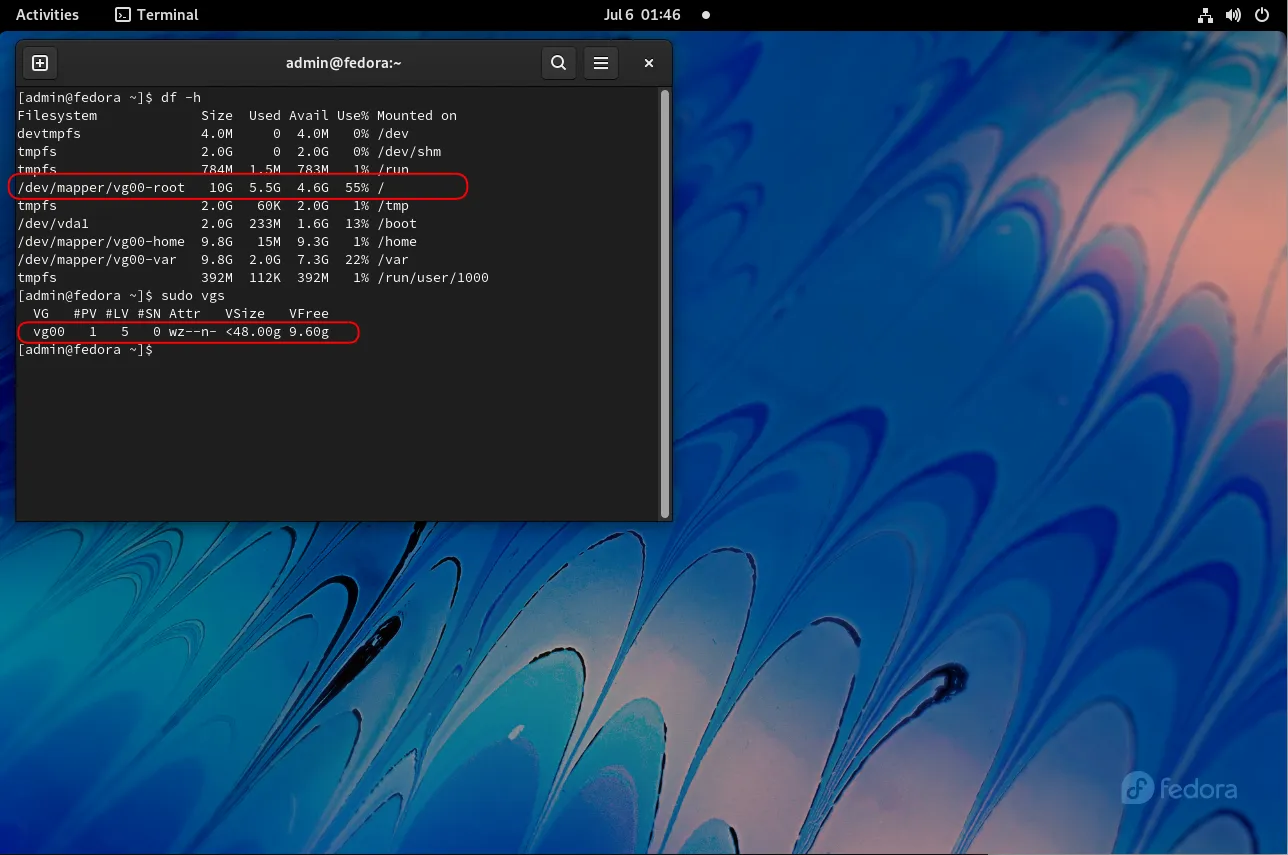
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
With your system prepared, you can now proceed with the upgrade. Follow these steps carefully to avoid any issues.
Install the DNF Plugin |
The DNF system upgrade plugin facilitates the upgrade process. Install it using the following command:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade
Download Fedora 37 Packages |
Next, download the Fedora 37 packages. This step can take some time, depending on your internet speed. Run the following command:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=37
Before you continue ensure that your system is fully upgraded by running "dnf --refresh upgrade".
Do you want to continue [y/N]: y
Press the y + Enter key to continue.
...
Multimedia
Common NetworkManager Submodules
Printing Support
Fedora Workstation product core
Transaction Summary
==================================================================================================================================
Install 127 Packages
Upgrade 1712 Packages
Downgrade 1 Package
Total download size: 1.9 G
DNF will only download packages, install gpg keys, and check the transaction.
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Press the y + Enter key to confirm and continue. This process may take some time to complete, depending on the number of installed packages and your system’s resources.
...
(1837/1840): yum-4.18.0-2.fc37.noarch.rpm 435 kB/s | 37 kB 00:00
(1838/1840): zchunk-libs-1.3.2-1.fc37.x86_64.rpm 500 kB/s | 51 kB 00:00
(1839/1840): zfs-fuse-0.7.2.2-28.fc37.x86_64.rpm 3.5 MB/s | 1.6 MB 00:00
(1840/1840): zenity-3.44.1-1.fc37.x86_64.rpm 4.5 MB/s | 3.2 MB 00:00
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 9.1 MB/s | 1.9 GB 03:29
Fedora 37 - x86_64 1.6 MB/s | 1.6 kB 00:00
Importing GPG key 0x5323552A:
Userid : "Fedora (37) <fedora-37-primary@fedoraproject.org>"
Fingerprint: ACB5 EE4E 831C 74BB 7C16 8D27 F55A D3FB 5323 552A
From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-fedora-37-x86_64
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Again, hit the y + Enter key to import the GPG key and continue.
If you encounter any dependency issues, use the --allowerasing option to resolve conflicts:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=37 --allowerasing
Key imported successfully
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
Complete!
Transaction saved to /var/lib/dnf/system-upgrade/system-upgrade-transaction.json.
Download complete! Use 'dnf system-upgrade reboot' to start the upgrade.
To remove cached metadata and transaction use 'dnf system-upgrade clean'
The downloaded packages were saved in cache until the next successful transaction.
You can remove cached packages by executing 'dnf clean packages'.
Initiate the Upgrade |
Once the packages are downloaded, start the upgrade process. Your system will reboot and begin upgrading to Fedora 37:
sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot
Your machine will reboot and begin the upgrade process. Be patient and do not interrupt the process or turn off your machine.
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
After the upgrade, there are a few tasks to complete to ensure everything is running smoothly.
Verify the Upgrade |
First, verify that your system is now running Fedora 37. Open a terminal and run:
cat /etc/fedora-release
You should see output indicating Fedora 37 has been installed.
Update All Packages |
Even though you’ve upgraded, it’s good practice to update all packages to ensure everything is current:
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
Reinstall Third-Party Repositories |
If you use third-party repositories, you may need to reinstall them. For example, to add RPM Fusion repositories:
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-37.noarch.rpm
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-37.noarch.rpm
Clean Up |
Finally, clean up unnecessary files to free up disk space
sudo dnf autoremove; sudo dnf clean all
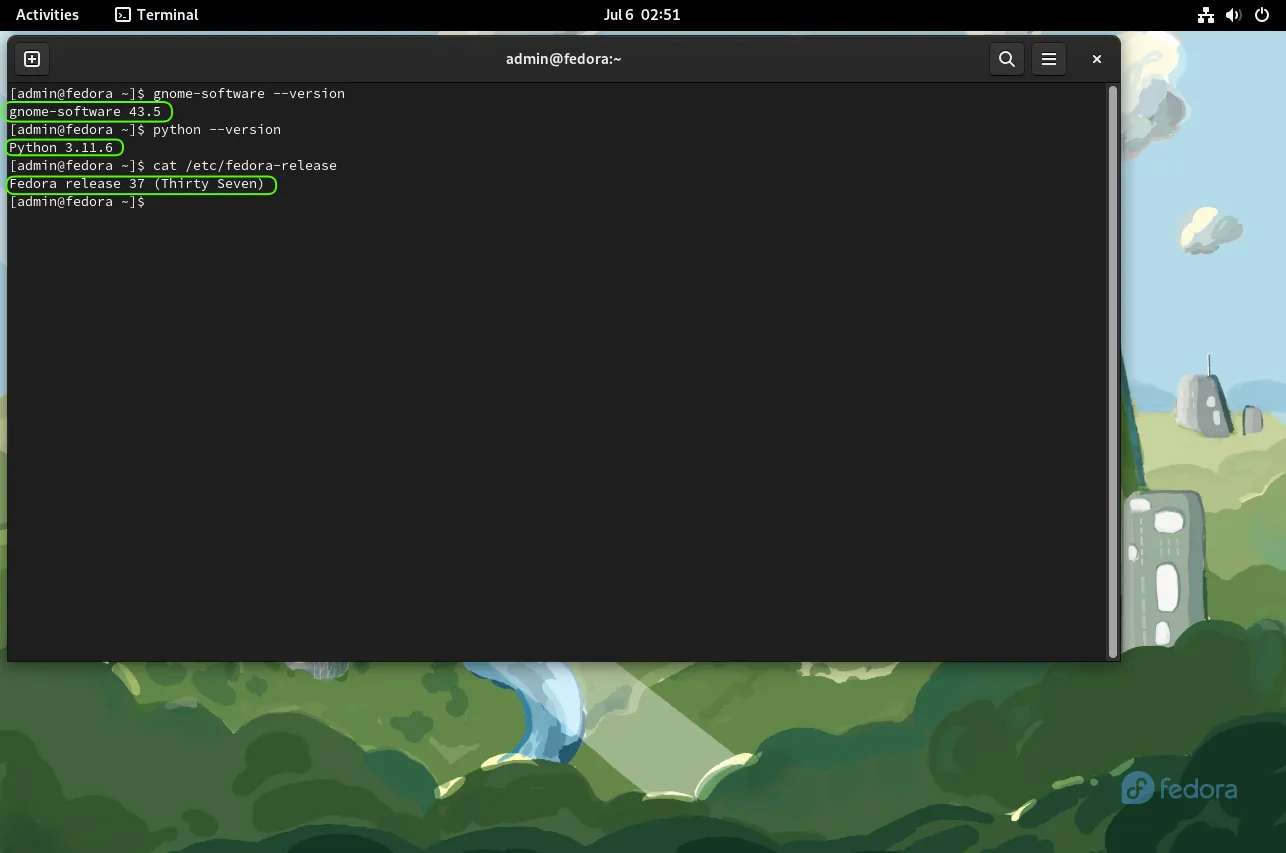
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
Some of the notable feature upgrades and enhancements include (but are not limited to): GNOME 43 and Python 3.11. For an in-depth look, visit the official Fedora 37 wiki page.
Upgrading can sometimes cause issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Boot Issues |
If your system fails to boot after the upgrade, try booting into an older kernel from the GRUB menu. Then, troubleshoot the problem by checking system logs:
journalctl -xe
Broken Packages |
If you encounter broken packages, try reinstalling them:
sudo dnf reinstall <package-name>
Network Issues |
If you experience network connectivity issues, restart the network manager:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
Upgrading from Fedora 35 to Fedora 37 is a straightforward process if you follow the steps outlined in this guide. Remember to back up your data, ensure your system is updated, and check disk space before starting the upgrade. Post-upgrade tasks, such as verifying the upgrade and reinstalling third-party repositories, will help you maintain a smooth-running system. If you encounter any issues, refer to the troubleshooting section for common solutions.
By keeping your Fedora system up-to-date, you benefit from the latest features, improved performance, and enhanced security. Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Backup Data | rsync -av --progress /home/user/ /path/to/backup/ |
| Update Fedora 35 | sudo dnf upgrade --refresh |
| Check Disk Space | df -h |
| Install DNF Plugin | sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade |
| Download Fedora 37 Packages | sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=37 |
| Initiate Upgrade | sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot |
| Verify Upgrade | cat /etc/fedora-release |
| Update All Packages | sudo dnf upgrade --refresh |
| Reinstall RPM Fusion Repositories | sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-37.noarch.rpm <br> sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-37.noarch.rpm |
| Clean Up | sudo dnf autoremove <br> sudo dnf clean all |
| Check System Logs | journalctl -xe |
| Reinstall Broken Packages | sudo dnf reinstall <package-name> |
| Restart Network Manager | sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager |
Following this guide ensures a smooth and successful upgrade to Fedora 37, allowing you to enjoy all the new features and improvements it offers.
Related Posts

Learn how to upgrade from Fedora 35 to Fedora 36 with our comprehensive step-by-step guide. Ensure a smooth transition with tips on preparing your system,

In this guide, we’ll walk you through the seamless process of migrating from Ubuntu 20.04 to 22.04, ensuring a smooth transition without losing any data
Discover the major differences between RHEL 8 and RHEL 9 and review the latest version’s enhancements in performance, security, and containerization support. RHEL 9 introduces
