
Are you looking to set up a Kubernetes development environment with Vagrant quickly and efficiently? Look no further! In this guide, we’ll walk through how

In this guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of installing Docker on Fedora 37, ensuring you’re ready to leverage its benefits efficiently.
In today’s fast-paced development environment, containerization has become an indispensable tool for software developers and system administrators alike. Docker, the leading containerization platform, empowers users to build, ship, and run applications seamlessly across different environments. If you’re running Fedora 37 and looking to harness the power of Docker, you’re in the right place.
Docker is an open-source platform that automates the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. These containers bundle the application code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and dependencies, allowing them to run reliably across any environment, from development to production. Docker’s containerization technology enables developers to package their applications with all the necessary components, ensuring consistency and eliminating the “it works on my machine” problem. Additionally, Docker provides tools for managing and orchestrating containers at scale, making it easy to deploy and manage complex applications in distributed environments.
Before diving into the installation process, it’s crucial to ensure that your Fedora 37 system is up to date. Open the terminal and execute the following command:
$ sudo dnf update -y
This command will update the package repositories and install any available updates for your system. It’s essential to have the latest packages to avoid compatibility issues during the Docker installation process.
Next, we need to install the necessary dependencies for Docker to function correctly on Fedora 37. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -y
This command will install the dnf-plugins-core package, which provides essential plugins for the DNF package manager. These plugins are required to enable the Docker repository on Fedora 37.
To install Docker on Fedora 37, we need to enable the official Docker repository. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo
This command adds the Docker CE repository to your system’s repository list, allowing you to install Docker Community Edition (CE) using DNF.
With the Docker repository enabled, you can now install the Docker Engine package. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
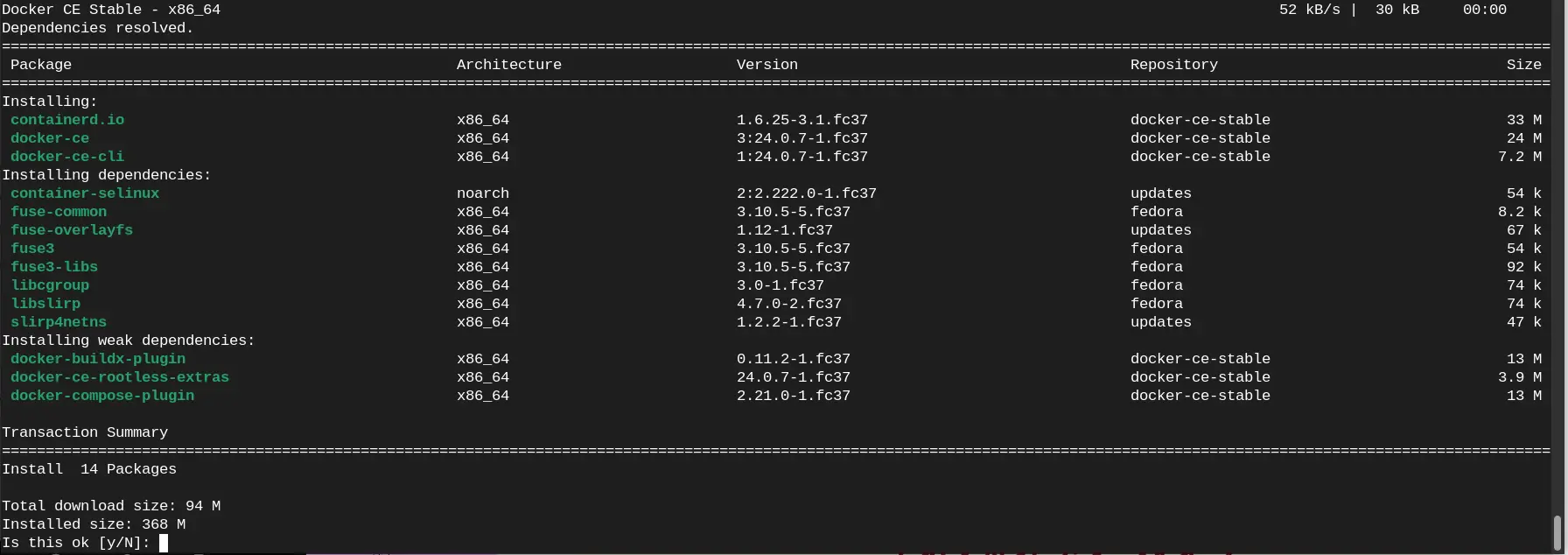
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
This command will install the Docker Engine, Docker CLI, and containerd.io packages on your Fedora 37 system. Once the installation is complete, the Docker service will start automatically.
To ensure that Docker starts automatically every time your system boots up, you need to enable the Docker service. Execute the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo systemctl enable --now docker
This command will start the Docker service immediately and enable it to start at boot time. You can verify that Docker is running correctly by executing the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status docker
If Docker is running without any errors, you’re all set to start using Docker on your Fedora 37 system.
To confirm that Docker is installed and functioning correctly on your Fedora 37 system, you can run a simple test by executing the following command in the terminal:
$ sudo docker run hello-world
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
c1ec31eb5944: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:4bd78111b6914a99dbc560e6a20eab57ff6655aea4a80c50b0c5491968cbc2e6
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
This command will download a small Docker image called “hello-world” and run it in a container. If everything is set up correctly, you should see a message confirming that your Docker installation is working correctly (as shown above).
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Docker on Fedora 37 and are now ready to leverage the power of containerization for your development and deployment workflows. By following the step-by-step instructions provided in this guide, you’ve gained the knowledge and skills necessary to harness the full potential of Docker on your Fedora 37 system.
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Related Posts

Are you looking to set up a Kubernetes development environment with Vagrant quickly and efficiently? Look no further! In this guide, we’ll walk through how
In this article, we compare and contrast both container platforms and ultimately decide whether to docker or not to podman. Table of Contents Introduction When

Troubleshooting made easy: Learn fixes and solutions for common Docker errors in this comprehensive guide. Enhance your container management skills and ensure seamless deployments. Table
