
In this article, we will review how to install minikube-v1.32.0 on RHEL9. This is the most recent stable release as of the date of this

Learn how to install Minikube on Ubuntu 24.04 with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover prerequisites, installation methods, resource management, and troubleshooting tips to set up your local Kubernetes environment effortlessly.
Minikube is an essential tool for developers looking to set up a local Kubernetes environment. If you’re running Ubuntu 24.04, installing Minikube can be straightforward if you follow the right steps. This guide will help you install Minikube efficiently while ensuring that your setup is optimized for performance and usability.
Minikube is an open-source tool that makes it easy to run Kubernetes locally. It creates a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your machine, which is perfect for testing and development. With Minikube, you can experiment with Kubernetes features without the complexity of a full-scale cluster.
Prerequisites |
Before installing Minikube, ensure you have the following:
Ubuntu 24.04: You can check your version using:
lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 24.04.1 LTS
Release: 24.04
Codename: noble
Virtualization Support: Ensure your CPU supports virtualization. You can check this with:
egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
4
If virtualization is supported, the output should return a number greater than zero.
Hardware Requirements: A minimum of 2GB RAM is recommended for running Minikube comfortably.
Minikube requires a hypervisor to run the virtual machine. The two most common options are KVM and VirtualBox.
Installing KVM |
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients bridge-utils
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
Add Your User to the KVM Group: |
sudo adduser $(whoami) kvm
info: Adding user `admin' to group `kvm' ...
Add Your User to the |
sudo usermod -aG libvirt $(whoami)
Also, ensure that /var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock is owned by your user.
sudo chown $(whoami): /var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock
Verify Installation: |
sudo systemctl status libvirtd
info: Adding user `admin' to group `kvm' ...
If you prefer VirtualBox, you can install it using the following commands:
Add VirtualBox Repository: |
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y software-properties-common && sudo add-apt-repository -y multiverse
Hit:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble InRelease
Hit:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-updates InRelease
Hit:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-security InRelease
Hit:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-backports InRelease
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
6 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
software-properties-common is already the newest version (0.99.48).
software-properties-common set to manually installed.
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 6 not upgraded.
Adding component(s) 'multiverse' to all repositories.
Hit:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble InRelease
Hit:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-updates InRelease
Hit:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-backports InRelease
Hit:4 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble-security InRelease
Reading package lists... Done
Install VirtualBox: |
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y virtualbox
Now that your virtualization software is set up, you can install Minikube.
Step 1: Download Minikube |
You can download the latest version of Minikube using curl (minikube version 1.34.0 as of the date of this publication):
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 99.0M 100 99.0M 0 0 79.9M 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 79.9M
Step 2: Install Minikube |
Next, move the binary to a directory included in your system’s PATH:
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Step 3: Verify Installation |
To confirm that Minikube is installed successfully, run:
minikube version
minikube version: v1.34.0
commit: 210b148df93a80eb872ecbeb7e35281b3c582c61
You should see the installed version of Minikube.
Now it’s time to start Minikube. You can choose the driver based on your virtualization software.
Starting Minikube with KVM |
minikube start --driver=kvm2
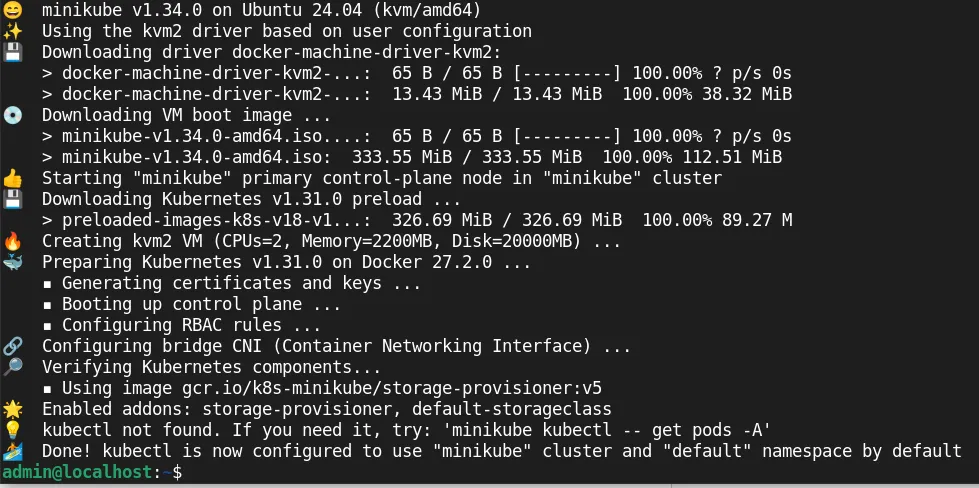
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
Starting Minikube with VirtualBox |
minikube start --driver=virtualbox
Configuring Resource Allocation |
You can also specify the number of CPUs and the amount of memory:
minikube start --cpus=2 --memory=2048 --driver=kvm2
Minikube includes kubectl , the command-line tool for interacting with Kubernetes clusters. To install kubectl :
Step 1: Install kubectl |
You can download the latest version of kubectl using curl (kubectl version 1.31.0):
curl -LO "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 53.7M 100 53.7M 0 0 76.1M 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 76.1M
Step 2: Make kubectl Executable |
chmod +x ./kubectl && sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Step 3: Verify kubectl Installation |
Run the following command to verify that kubectl is installed:
kubectl version --client
Client Version: v1.31.0
Kustomize Version: v5.4.2
Once Minikube is running, you can manage it using various commands.
Checking Cluster Status |
To check the status of your Minikube cluster, use:
minikube status
minikube
type: Control Plane
host: Running
kubelet: Running
apiserver: Running
kubeconfig: Configured
Stopping Minikube |
When you’re done, you can stop the Minikube cluster with:
minikube stop
Deleting Minikube Cluster |
To delete the Minikube cluster and free up resources:
minikube delete
Issue: Minikube Fails to Start |
If Minikube fails to start, check if your virtualization software is running correctly. Ensure that your user is part of the kvm group for KVM as well as libvirt. Double-check the libvirt-sock file to ensure it is also owned by your user.
Issue: kubectl Not Found |
If kubectl is not found, ensure that it is in your PATH. You can check your PATH with:
echo $PATH
If /usr/local/bin is not listed, you may need to add it to your shell configuration file (e.g. .bashrc if you’re using bash or .zshrc if your using zsh.)
export PATH="/usr/local/bin:$PATH"
Issue: Insufficient Resources |
If you encounter resource-related issues, consider adjusting the CPU and memory settings when starting Minikube:
minikube start --cpus=4 --memory=4096
Installing Minikube on Ubuntu 24.04 is a straightforward process that opens up a world of possibilities for local Kubernetes development. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can set up your environment, run a Kubernetes cluster, and begin developing your applications with ease. Remember, local development with Kubernetes can be resource-intensive, so monitor your system’s performance and adjust configurations as needed.
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.

In this article, we will review how to install minikube-v1.32.0 on RHEL9. This is the most recent stable release as of the date of this
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of creating and deploying a LAMP stack on Minikube, a tool that enables you to

In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of deploying WordPress on Minikube, enabling you to develop and test your WordPress sites with ease.
