
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through the process of deploying a MySQL database using Podman, covering installation, configuration, and best practices. Table of Contents

Learn how to install Podman on Ubuntu 24.04 Server with this comprehensive guide. Discover key features, essential commands, and troubleshooting tips to effectively manage your containers securely and efficiently. Perfect for developers and system administrators looking for a Docker alternative!
Are you looking to harness the power of containers without the overhead of Docker? Podman is an excellent alternative that allows you to manage containers easily and securely. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process to install Podman on your Ubuntu 24.04 Server. We’ll also cover its key features, common commands, and how to troubleshoot any issues you might encounter. By following this guide, you’ll be well on your way to leveraging container technology for your applications.
Podman (Pod Manager) is an open-source container management tool that allows you to create, manage, and run OCI containers. Unlike Docker, Podman operates as a daemonless tool, meaning it doesn’t require a long-running service to manage containers. This feature enhances security and simplifies operations, especially in environments where resources are limited.
Key Features of Podman |
Before we begin the installation process, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Ubuntu 24.04 Server |
| RAM | Minimum 1 GB (2 GB recommended) |
| Disk Space | At least 1 GB free |
| Network | Internet access |
Step 1: Update Your System |
It’s always a good idea to start with an updated system. Open your terminal and execute the following commands:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install Required Packages |
Podman requires a few dependencies. Install them using the command:
sudo apt install -y software-properties-common
Step 3: Install Podman |
You can now install Podman directly from the official repositories:
sudo apt install -y podman
Step 4: Verify Installation |
Check if Podman was installed correctly:
podman --version
podman version 4.9.3
You should see the version number, confirming the installation.
You can now use Podman with these basic commands. Here are a few examples:
Pull an Image |
To pull a container image, use:
podman pull docker.io/library/ubuntu
Trying to pull docker.io/library/ubuntu:latest...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob ff65ddf9395b done |
Copying config 59ab366372 done |
Writing manifest to image destination
59ab366372d56772eb54e426183435e6b0642152cb449ec7ab52473af8ca6e3f
To list all pulled images, use:
podman images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
docker.io/library/ubuntu latest 59ab366372d5 5 days ago 80.6 MB
Run a Container |
To run a simple Ubuntu container:
podman run -it ubuntu /bin/bash
root@44d532be97a3:/#
List Running Containers |
To list all running containers:
podman ps
To list all running containers (including stopped ones):
podman ps -a
Inspecting a Container |
To get detailed information about a specific container, use the podman inspect command. This command provides comprehensive details, including configuration settings and state information:
podman inspect <container_id_or_name>
For example:
podman inspect ubuntu
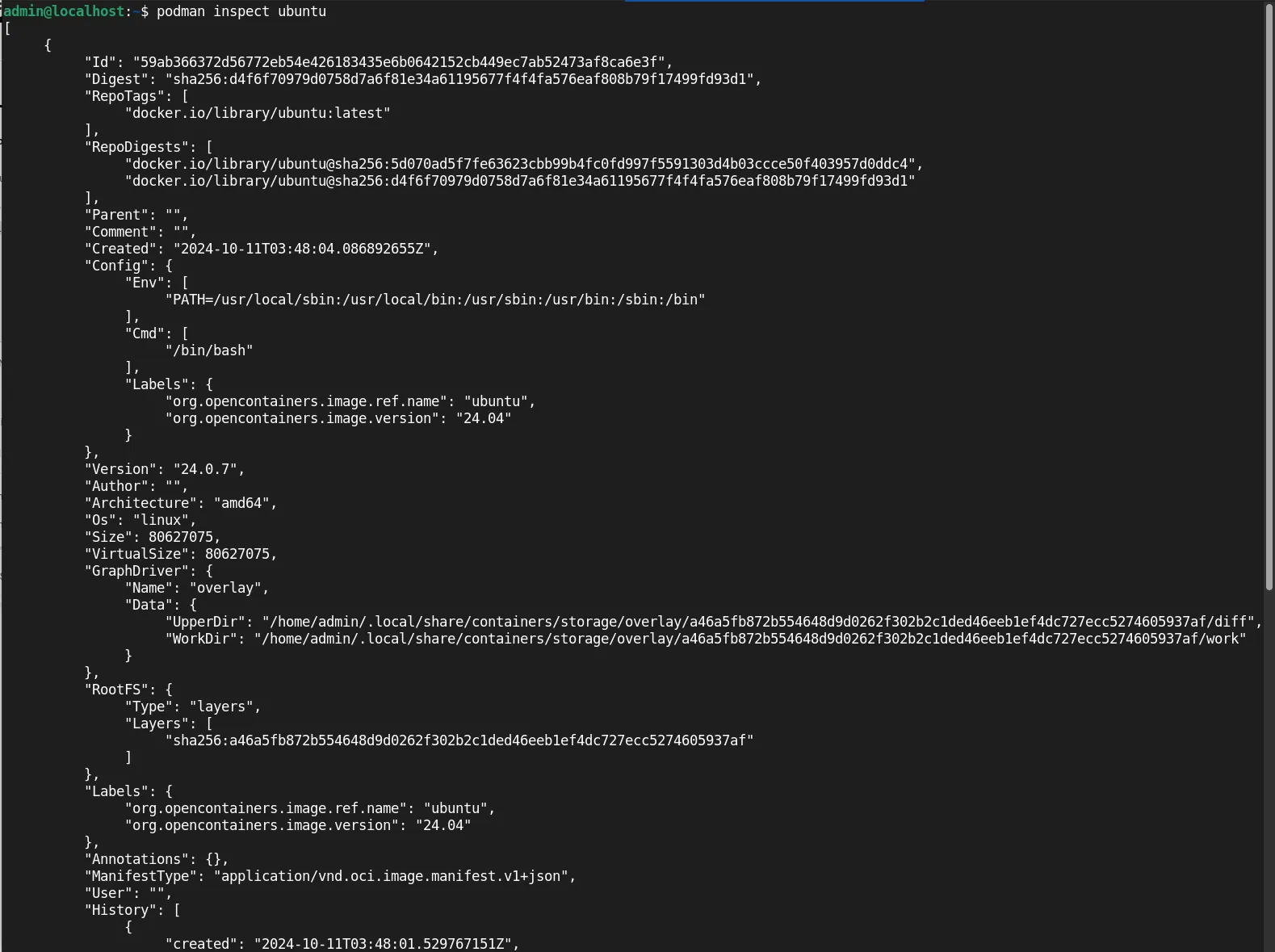
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
This command outputs a JSON-formatted summary of the container’s configuration, environment variables, and runtime status, which can be extremely useful for debugging and understanding how your container is set up.
Stopping a Container |
To stop a running container, first find its ID or name using podman ps, then run:
podman stop <container_id_or_name>
Removing a Container |
To remove a stopped container:
podman rm <container_id_or_name>
Running Containers in Detached Mode |
To run a container in detached mode, add the -d flag:
podman run -d ubuntu sleep 1000
One of the unique features of Podman is its ability to manage pods. A pod is a group of one or more containers. Here’s how you can create and manage pods:
Creating a Pod |
To create a new pod:
podman pod create --name mypod
Running Containers in a Pod |
To run a container in the newly created pod:
podman run -d --pod mypod ubuntu sleep 1000
Listing Pods |
To list all pods:
podman pod ps
POD ID NAME STATUS CREATED INFRA ID # OF CONTAINERS
872290dd8cab mypod Running 5 mins ago 3768d84bdabf 1
Issue: Podman Not Starting |
If Podman doesn’t start, ensure you have the necessary permissions and podman installed.
Issue: Container Fails to Run |
If a container fails to start, check the logs using:
podman logs <container_id_or_name>
Issue: Network Issues |
Ensure your server has proper network access, especially if you are pulling images from external registries.
Installing Podman on Ubuntu 24.04 Server is a straightforward process that equips you with a powerful tool for managing containers efficiently. With its daemonless architecture and rootless capabilities, Podman stands out as a versatile solution for container management.
Recap of Steps |
Podman is an excellent alternative to Docker, providing a simpler and more secure approach to container management. Whether you’re developing applications or managing microservices, Podman is worth considering.
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts and share this post!

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through the process of deploying a MySQL database using Podman, covering installation, configuration, and best practices. Table of Contents
This guide examines how to setup an HTTPS server using Podman, a containerization tool, thereby fortifying a secure and streamlined hosting environment for your web

In this guide, we’ll explore how to host your own Podman repository, empowering you with greater control over your container images. Table of Contents Introduction
