
Learn how to install Nice DCV on Ubuntu 24.04 with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover essential commands, configuration tips, and troubleshooting advice to optimize your

Discover 10 effective tips for optimizing your Ubuntu/Debian system’s performance. Learn how to optimize boot times, manage system resources, and keep your system running smoothly with practical examples.
Ubuntu and Debian are two of the most popular Linux distributions, known for their reliability, security, and flexibility. However, even these robust operating systems can benefit from regular maintenance and optimization to improve performance. Whether you’re using your system for personal use, development, or server applications, optimizing performance is key to getting the most out of your machine.
In this post, we’ll explore 10 essential tips for enhancing the speed, efficiency, and responsiveness of your Ubuntu/Debian system. These strategies focus on optimizing boot times, memory usage, disk performance, and general system resource management.
1. Update Your System Regularly |
Keeping your system up-to-date is one of the most basic yet important steps for optimizing performance. Updates often include security patches, bug fixes, and new software features that can improve the overall speed of your machine.
How to Update Your System |
Run the following commands in your terminal to update all packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt dist-upgrade
sudo apt autoremove
|
|
|
|
2. Enable and Use Swap Space |
Swap space acts as virtual memory when your physical RAM is full. Enabling and properly configuring swap space ensures that your system won’t slow down or crash when memory demand increases.
Checking for Swap |
To check if swap is enabled:
swapon --show
If no output is shown, you can create a swap file using the following steps.
Create a Swap File |
sudo fallocate -l 4G /swapfile # Create a 4GB swap file
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile # Set proper permissions
sudo mkswap /swapfile # Set up the swap file
sudo swapon /swapfile # Enable the swap file
Make Swap Permanent |
Add the following line to your /etc/fstab file:
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
3. Optimize Boot Time with Systemd-analyze |
A slow boot time can be frustrating. Ubuntu/Debian systems use systemd to manage boot processes. You can optimize boot time by analyzing and reducing startup services.
Analyze Boot Performance |
To see how long your system takes to boot, use:
systemd-analyze
Startup finished in 4.042s (kernel) + 44.438s (userspace) = 48.481s
graphical.target reached after 44.393s in userspace.
It will show a summary of the boot process, including the time spent in firmware, the kernel, and the user space.
Examine Boot Logs |
For more detailed insights, run:
systemd-analyze blame
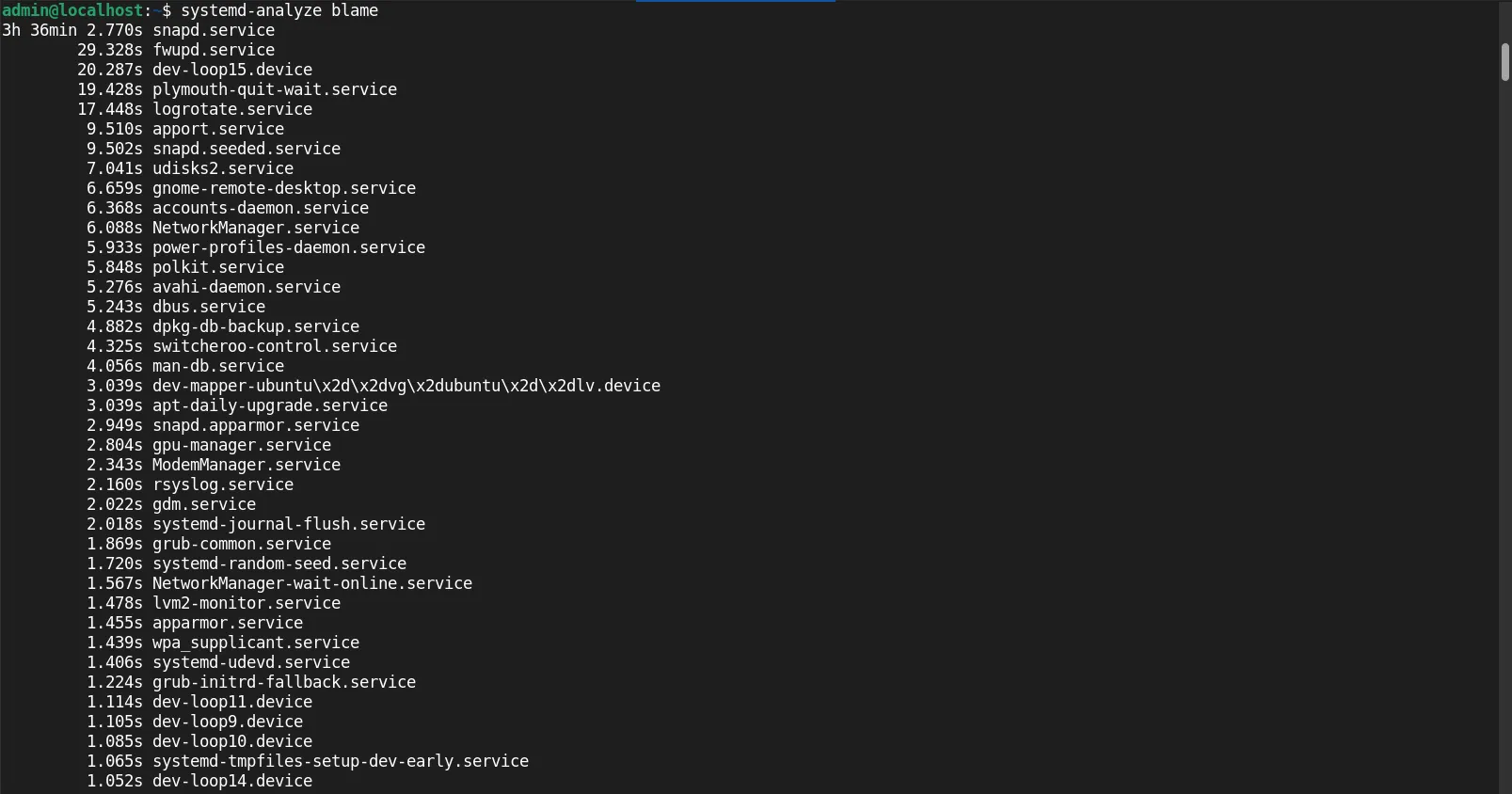
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
This command lists all services and their startup times. Identify services that can be delayed or disabled to speed up boot time.
4. Use a Lightweight Desktop Environment (DE) |
The desktop environment (DE) can have a significant impact on system performance. Lightweight DEs like XFCE, LXQt, and MATE use fewer resources compared to heavier environments like GNOME and KDE Plasma.
Installing XFCE |
sudo apt install xfce4
Once installed, you can log out, choose XFCE from the login screen, and enjoy a snappy, resource-efficient desktop.
5. Optimize Your Startup Applications |
Unnecessary startup applications can consume valuable resources and slow down your system. Disable or remove non-essential applications that load at startup.
Manage Startup Applications |
Alternatively, use the command line:
gnome-session-properties
This allows you to manage which applications are started automatically when you log in.
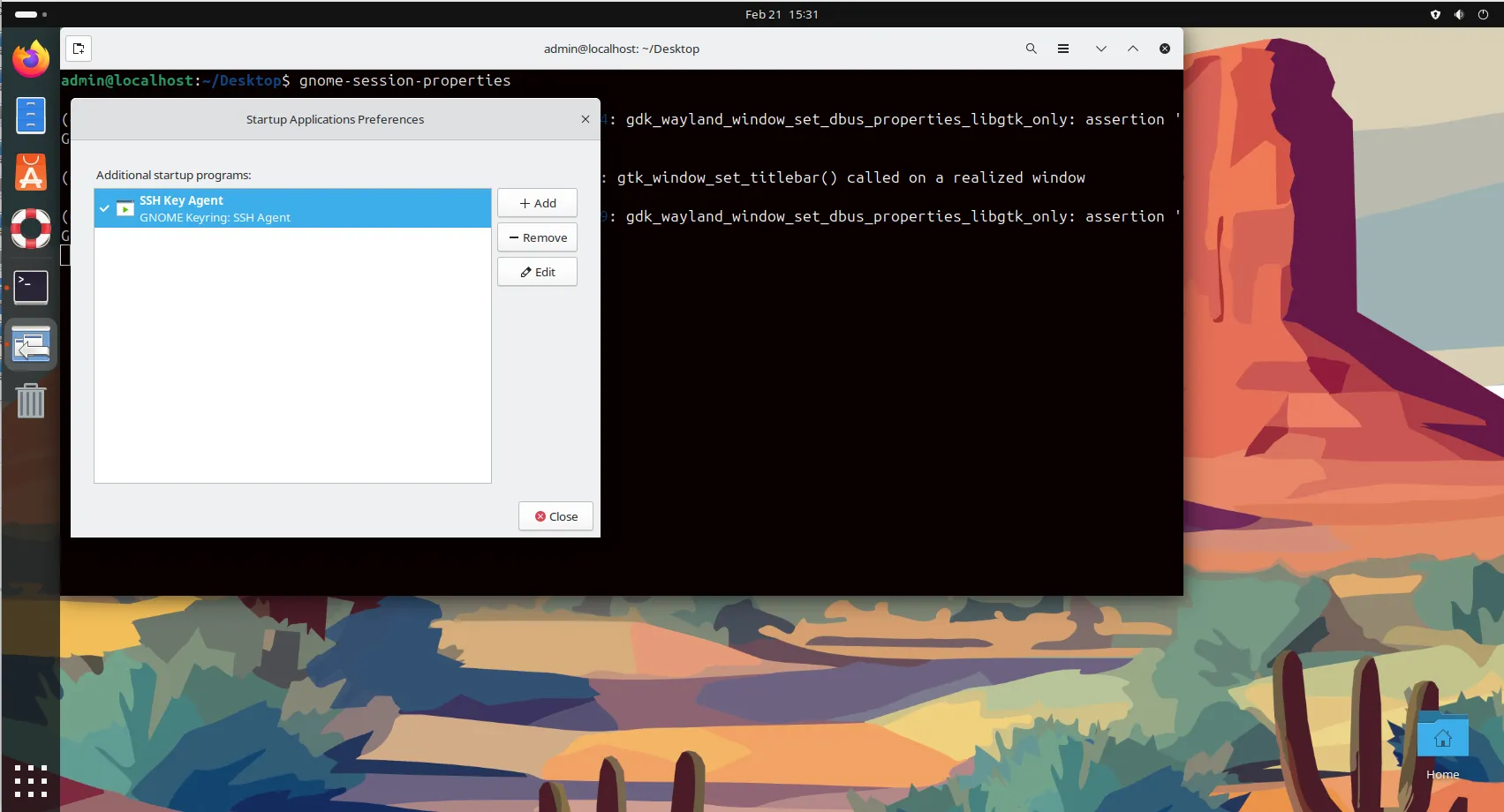
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
6. Clean Up and Remove Unnecessary Files |
Old, unused files can accumulate over time, consuming disk space and system resources. Regularly cleaning your system is crucial to keeping it running efficiently.
gnome-session-properties
Remove Old Packages |
sudo apt autoremove
This command will automatically remove old and unused packages that are no longer required.
Clear Cache |
To remove unnecessary cached files, use:
sudo apt clean
You can also use BleachBit for a more thorough cleaning of your system.
Caution: While BleachBit is a powerful tool, it can potentially harm your system if used incorrectly. It’s highly effective, but make sure to carefully select the options you use. Always take snapshots or backups before running it to avoid any unintended issues.
Clear Systemd Logs |
Systemd logs can grow over time and take up significant space. To clear these logs:
sudo journalctl --vacuum-time=7d
This command will delete logs older than 7 days.
7. Optimize Disk Performance with SSD Trim |
If you’re using an SSD (Solid State Drive), enabling SSD trim will help maintain its performance by regularly clearing unused blocks.
Check SSD Support |
lsblk --discard
Enable SSD Trim |
If your SSD supports trimming, add the following line to /etc/fstab:
UUID=<your-ssd-uuid> none discard
To manually trim your SSD, you can run:
sudo fstrim -v /
8. Reduce Swappiness for Better Performance |
The swappiness value determines how often your system uses swap space. A higher value means the system will prefer to swap out data to disk, even when there’s available RAM. A lower value keeps data in RAM longer.
Check Current Swappiness |
cat /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
By default, the value is usually set to 60. To reduce it, for example to 10:
sudo sysctl vm.swappiness=10
Make the Change Permanent |
Add the following line to your /etc/sysctl.conf:
vm.swappiness=10
9. Monitor System Resources with htop |
htop is an interactive process viewer that provides real-time insights into your system’s resource usage, including CPU, memory, and disk activity. It’s an excellent tool for diagnosing performance bottlenecks.
Install htop |
sudo apt install htop
To run htop, simply type:
htop
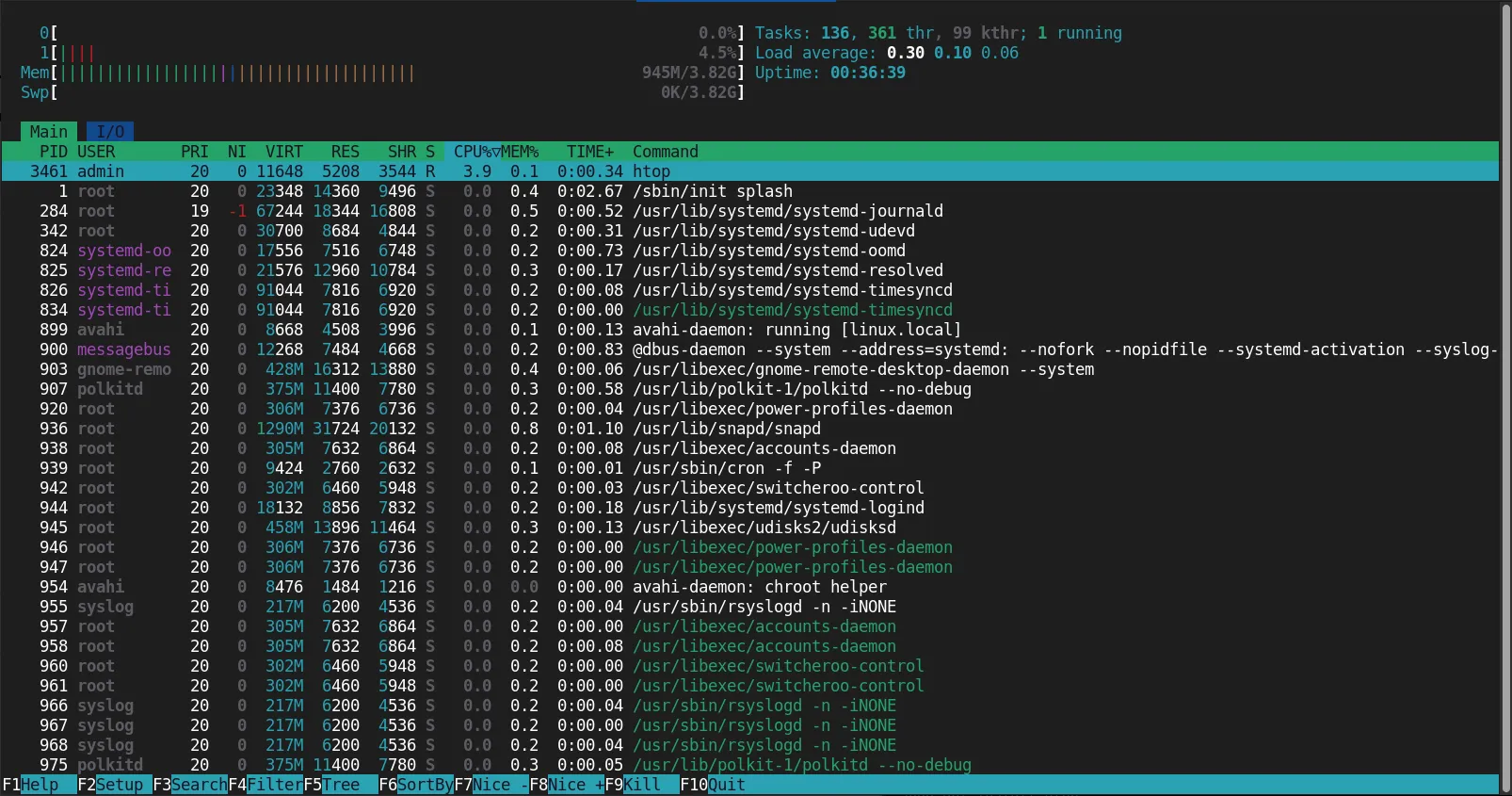
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
This will open a terminal-based graphical interface showing your system’s resource usage. You can interactively manage processes, kill tasks, and sort them by resource consumption.
10. Install and Use a Performance Tuning Tool |
For advanced users, tools like tuned and cpupower can help adjust CPU and power settings for better performance or battery life.
Install and Enable |
sudo apt install tuned
sudo systemctl enable --now tuned
Once installed, you can use profiles like balanced, powersave, and throughput-performance for different use cases.
CPU Frequency Scaling with cpupower |
To adjust the CPU frequency scaling, install cpupower:
sudo apt install linux-tools-common linux-tools-generic
Then, to set your CPU to the highest performance:
sudo cpupower frequency-set --governor performance
Optimizing your Ubuntu/Debian system can significantly improve your overall user experience. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can speed up your system, free up valuable resources, and ensure your machine runs as efficiently as possible. Regular system updates, memory management, cleaning up unnecessary files, and tuning startup services can all make a noticeable difference.
Keep your system lean, fast, and reliable with these simple optimizations, and your Ubuntu/Debian experience will be smooth and snappy!
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share this post!

Learn how to install Nice DCV on Ubuntu 24.04 with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover essential commands, configuration tips, and troubleshooting advice to optimize your

Learn how to install LibreOffice on Ubuntu 24.04 with step-by-step instructions for different methods, including APT, PPA, Snap, and Flatpak. Get the latest version or

Learn how to install and configure Google Chrome Remote Desktop on Ubuntu 24.04 with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Ensure secure and efficient remote access to
