
In this article, we will be comparing Ansible, Terraform, and Pulumi–three popular IaC tools, to help you choose the best option for your projects. Table

In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to install Webmin on RHEL 9 or CentOS 9, ensuring smooth server management with ease.
Managing a server efficiently often requires robust administrative tools that streamline tasks and provide a user-friendly interface. Webmin is one such tool, offering a comprehensive web-based administration platform for Linux servers.
Webmin, initially released in 1997 by Jamie Cameron, quickly gained popularity as a powerful web-based system administration tool for Unix-like systems.
Over the years, Webmin has evolved into a feature-rich platform, offering administrators a graphical interface to manage various aspects of their servers, including user accounts, file systems, network configurations, and more. Its modular design allows for easy extension with additional modules, catering to a wide range of server management needs.
Despite its longevity, Webmin continues to receive regular updates and improvements, ensuring compatibility with modern Linux distributions and addressing security vulnerabilities. Its active community of developers and users contributes to its ongoing development and maintenance, making it a reliable choice for server administration tasks.
For illustrative purposes, we’ve configured our system with the following settings (set yours according to your environment):
| Hostname | testsrv1.localdomain |
| Public IP address | 192.168.1.240 (Private IP: 10.0.2.15) |
| RAM | 2 |
| Cores | 2 |
Now, let’s dive into the installation process of Webmin on your RHEL 9 or CentOS 9 server.
Before proceeding with the installation of Webmin, it’s essential to ensure that your system is up-to-date. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
$ sudo dnf update -y
This will update your system with the latest packages and security patches, ensuring a stable environment for Webmin installation.
Webmin relies on several dependencies to function correctly. Install them by executing the following command:
$ sudo dnf install perl perl-CPAN perl-App-cpanminus perl-Digest-SHA perl-Net-SSLeay perl-Data-Dumper
Next, download the latest version of Webmin from the official website or repository. You can use wget or curl to download the package (most recent version as of the date of this publication) directly to your system. For example:
$ wget https://github.com/webmin/webmin/releases/download/2.105/webmin-2.105-1.noarch.rpm
Once the package is downloaded, install it using the dnf package manager:
$ sudo dnf install ./webmin-2.105-1.noarch.rpm
This command will install Webmin along with its dependencies on your system.
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:04 ago on Tue 30 Jan 2024 02:02:25 AM UTC.
Dependencies resolved.
===============================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
===============================================================================================
Installing:
webmin noarch 2.105-1 @commandline 39 M
Installing dependencies:
redhat-indexhtml noarch 9-4.el9_2 rhel-9-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms 245 k
Installing weak dependencies:
lynx x86_64 2.8.9-19.el9 rhel-9-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms 1.6 M
perl-Encode-Detect x86_64 1.01-37.el9 rhel-9-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms 94 k
shared-mime-info x86_64 2.1-5.el9 rhel-9-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms 561 k
Transaction Summary
===============================================================================================
Install 5 Packages
Total size: 41 M
Total download size: 2.4 M
Installed size: 127 M
Is this ok [y/N]: y
After the installation is complete, start the Webmin service using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start webmin
You can also enable the service to start automatically on system boot:
$ sudo systemctl enable webmin
Now lets open the Webmin port (10000) for access by running the following commands:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10000/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Webmin should now be up and running on your server. Open a web browser and navigate to the following address:
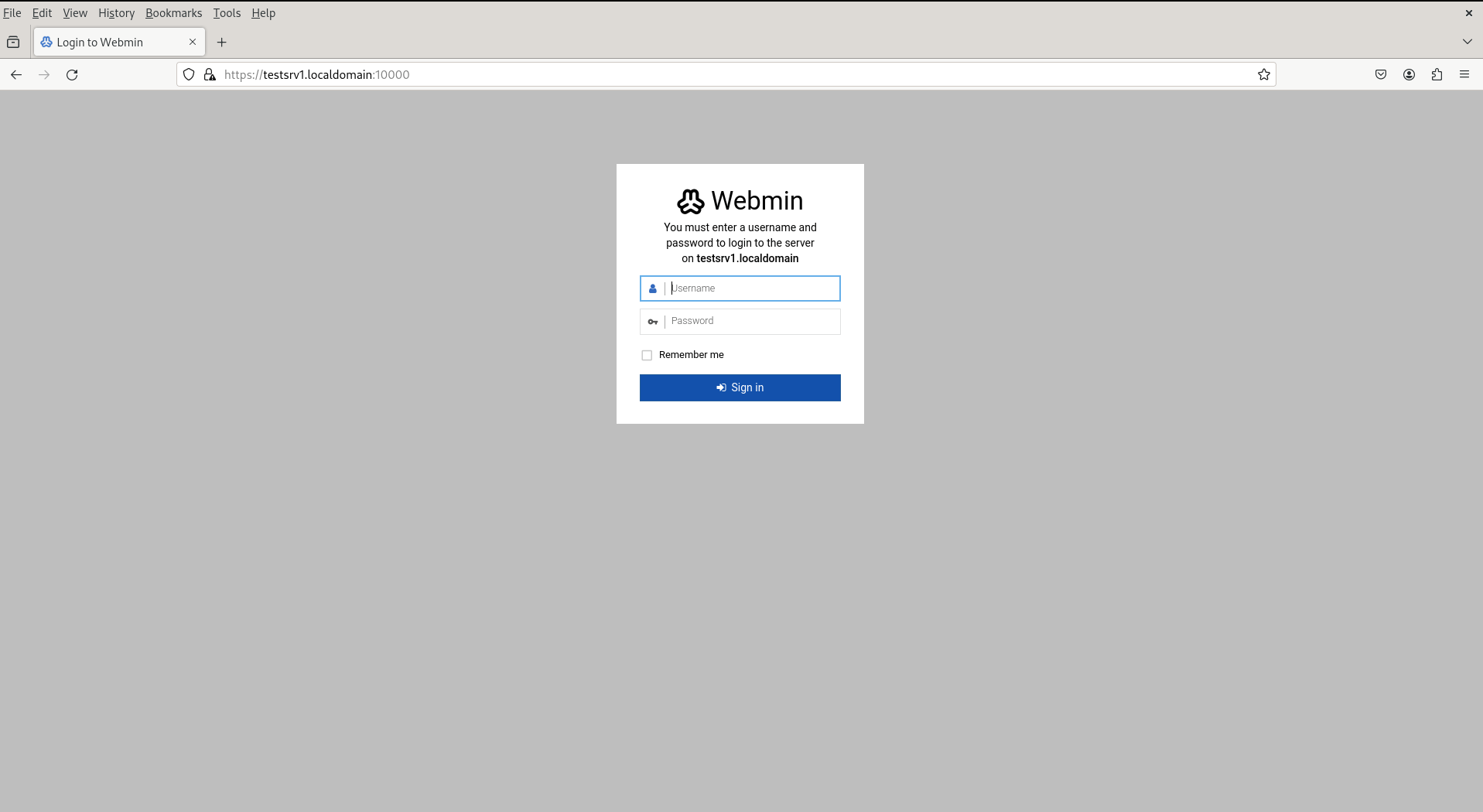
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
Replace your_server_ip or hostname with the actual IP address or hostname of your server. You will be greeted with the Webadmin login screen.
Use the root credentials of your server to log in to the Webadmin interface. Once logged in, you can configure various aspects of your server, including users, services, firewall settings, and more, through the intuitive Webadmin dashboard.
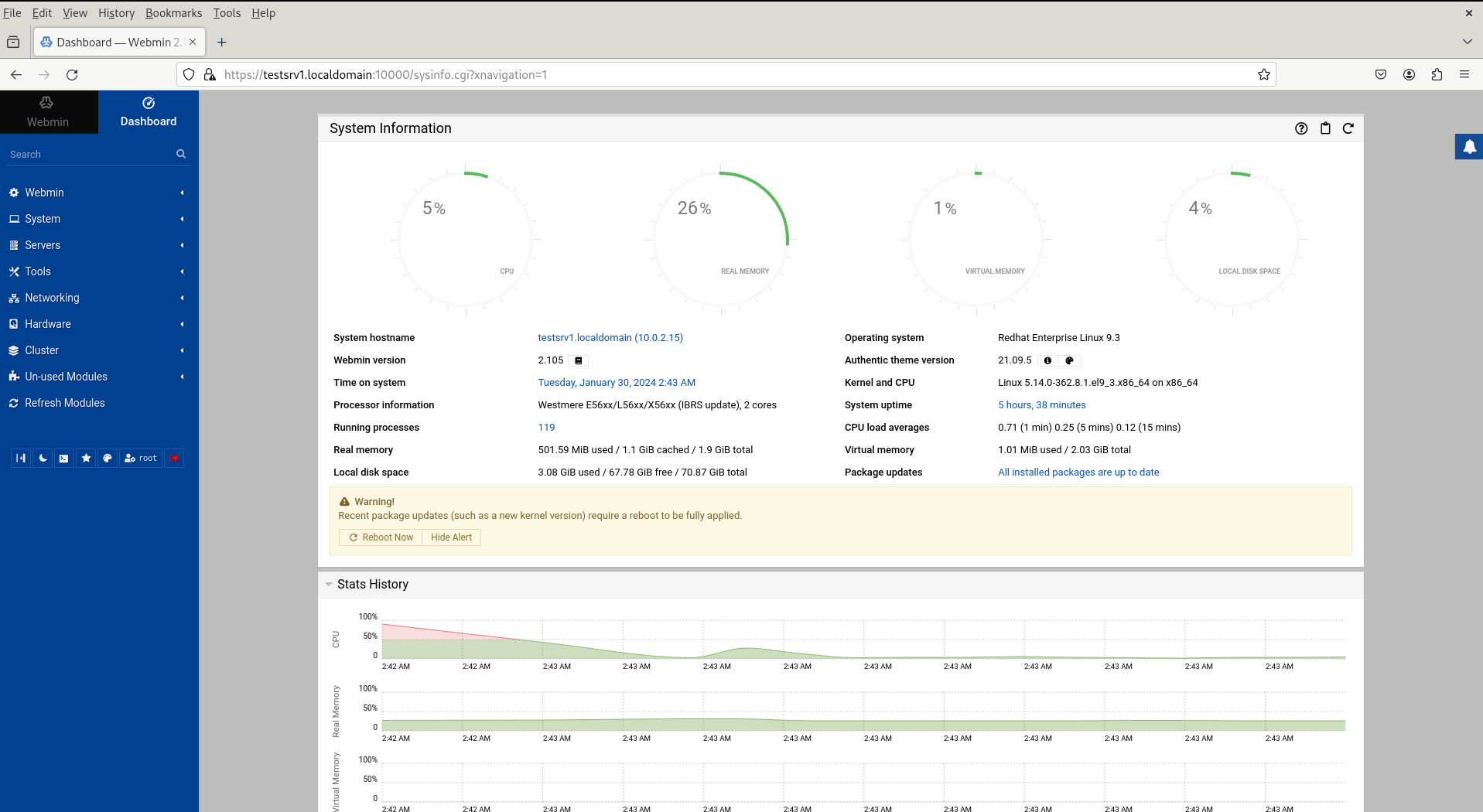
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
With Webmin installed on your RHEL 9 or CentOS 9 server, you now have a powerful web-based administration tool at your disposal. By following this step-by-step guide, you can streamline server management tasks and ensure optimal performance with ease. Take advantage of Webmin’s robust features to simplify administrative tasks and enhance your server’s efficiency.
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Related Posts

In this article, we will be comparing Ansible, Terraform, and Pulumi–three popular IaC tools, to help you choose the best option for your projects. Table

In this guide, we’ll walk you through the seamless process of migrating from Ubuntu 20.04 to 22.04, ensuring a smooth transition without losing any data

In this article, we will review installing and using Git on Linux machines. Besides minor differences in syntax, the install commands and procedures are similar
