
Configuring autofs in Linux is a straightforward task. This article will guide you through the process of setting up and enabling the autofs service. Table

Learn how to securely deploy GFS2 on encrypted volumes over multipath storage in a high-availability Linux cluster. Includes CLI examples, automation tips, and best practices.
In modern enterprise IT environments, the need for secure, resilient, and high-availability storage systems is more critical than ever. Combining GFS2, multipath storage, and LUKS encryption provides a powerful solution that enables shared, encrypted block storage access across multiple Linux nodes. This blog post guides you step-by-step through the setup process and best practices for deploying GFS2 on encrypted volumes in a clustered multipath environment.
GFS2 (Global File System 2) is a clustered file system developed by Red Hat. It allows multiple nodes in a cluster to simultaneously access and write to the same file system on a shared block device.
💡 Why Use GFS2? |
|
|
|
|
|
Below is a diagram representing the architecture of GFS2 with encrypted volumes and multipath:
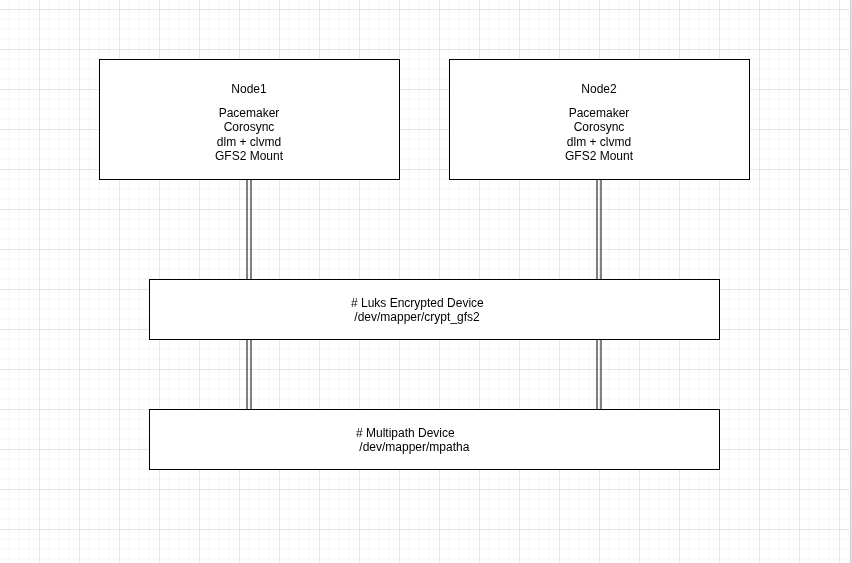
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| OS | RHEL, CentOS, Rocky Linux 8/9 |
| Packages | pcs, gfs2, lvm2, cryptsetup, fence-agents |
| Shared storage | SAN LUN visible via multipath |
| Cluster software | Pacemaker, Corosync |
| Security | LUKS encryption for block devices |
| Fencing | Essential for GFS2 integrity |
Install Required Packages on All Nodes |
Become the root user, and execute the following command:
dnf install -y pcs gfs2 lvm2-cluster cryptsetup fence-agents
Start pcsd and enable autostart upon reboot:
systemctl enable --now pcsd
Authenticate Cluster Nodes |
echo MySecret | passwd hacluster
pcs host auth node1 node2 -u hacluster -p MySecret
Create and Start the Cluster |
pcs cluster setup --name gfs2cluster node1 node2
pcs cluster start --all
pcs cluster enable --all
Enable Cluster Services and Fencing |
pcs property set stonith-enabled=true
pcs resource create dlm ocf:pacemaker:controld op monitor interval=30s
pcs resource create clvmd ocf:heartbeat:clvm op monitor interval=30s
Encrypt the Shared Multipath Device |
On one node only:
cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/mapper/mpatha
cryptsetup open /dev/mapper/mpatha crypt_gfs2
Create LVM on Encrypted Device |
pvcreate /dev/mapper/crypt_gfs2
vgcreate vg_gfs2 /dev/mapper/crypt_gfs2
lvcreate -n lv_gfs2 -L 20G vg_gfs2
Format with GFS2 |
mkfs.gfs2 -p lock_dlm -t gfs2cluster:mygfs2fs -j 2 /dev/vg_gfs2/lv_gfs2
Mount on All Nodes |
mkdir -p /gfs2
echo "/dev/vg_gfs2/lv_gfs2 /gfs2 gfs2 _netdev 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
mount -a
View Active Multipath Devices |
multipath -ll
Recommended |
devices {
filter = [ "a|/dev/mapper/mpath.*|", "r|/dev/sd.*|", "r|.*|" ]
multipath_component_detection = 1
}
This ensures LVM ignores raw devices and only uses valid multipath mappers.
Each node must manually or automatically unlock the encrypted device before the GFS2 mount happens.
Manual Unlock |
cryptsetup open /dev/mapper/mpatha crypt_gfs2
Use /etc/crypttab on all nodes:
crypt_gfs2 /dev/mapper/mpatha none luks
You can also automate this using Clevis + Tang or key escrow systems for enterprise environments.
| Scenario | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Node crashes | Pacemaker detects failure |
| Fencing is triggered | Node is forcibly rebooted or powered off |
| Surviving nodes | Continue I/O normally if fencing succeeds |
| No fencing | I/O to GFS2 freezes on all nodes to prevent corruption |
Check Node Status |
pcs status
dmesg | grep gfs2
| Layer | Device/Command | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | /dev/mapper/mpatha | Multipath LUN |
| Encrypted | /dev/mapper/crypt_gfs2 | LUKS device |
| LVM | vg_gfs2, lv_gfs2 | Shared VG across nodes |
| Filesystem | GFS2 | Cluster-aware FS |
| Cluster | Pacemaker + DLM | Handles quorum and locking |
Q1: Can I use XFS or ext4 with shared encrypted LUNs? |
❌ No — they’re not cluster-aware. Use GFS2 or OCFS2 only.
Q2: Can two nodes mount the same encrypted volume? |
✅ Yes, but only after all have unlocked the LUKS device.
Q3: Is fencing mandatory? |
✅ Yes. GFS2 requires fencing for safety against split-brain and data corruption.
Deploying GFS2 on encrypted multipath volumes provides a robust, secure, and high-availability shared storage setup suitable for critical workloads. However, it’s crucial to:
|
Did you find this article helpful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Feel free to share this post with those who may benefit, and let us know your thoughts in the comments section below.

Configuring autofs in Linux is a straightforward task. This article will guide you through the process of setting up and enabling the autofs service. Table

NFS or Network File System is a commonly known method for network file sharing on Linux hosts. We will create and export an NFS server.

Learn how to manage GPT and MBR partitions in Linux using powerful CLI tools like fdisk, gdisk, and parted. This guide covers creating, deleting, resizing,
