
Explore the differences between Virtualbox and KVM in this comprehensive comparison. Discover which virtualization solution suits your needs best, whether you prioritize ease of use or top-notch performance. Dive into key features, performance capabilities, and use cases to make an informed decision.
In the realm of virtualization, two heavyweights often stand out: Virtualbox and KVM. Both are powerful tools for running multiple operating systems on a single host machine, but they come with their own set of features, performance capabilities, and use cases. So, let’s dive in and explore the key differences between Virtualbox and KVM to help you choose the right one for your needs.
Virtualbox, developed by Oracle, is renowned for its user-friendly interface and ease of use. It’s a type 2 hypervisor, meaning it runs on top of an existing operating system like Windows, macOS, or Linux. This makes it accessible to a wide range of users, from beginners to experienced professionals.
One of the standout features of Virtualbox is its extensive support for guest operating systems. Whether you need to run Windows, Linux, macOS, or even experimental systems like Haiku or ReactOS, Virtualbox has you covered. Additionally, Virtualbox offers a variety of features such as snapshotting, shared folders, and seamless mode, which allows you to integrate guest applications with your host desktop.
However, Virtualbox may not be the best choice for performance-intensive tasks. Since it runs as a user-space application, it can suffer from overhead compared to bare-metal hypervisors like KVM. This can result in slightly lower performance, especially when running resource-intensive workloads.
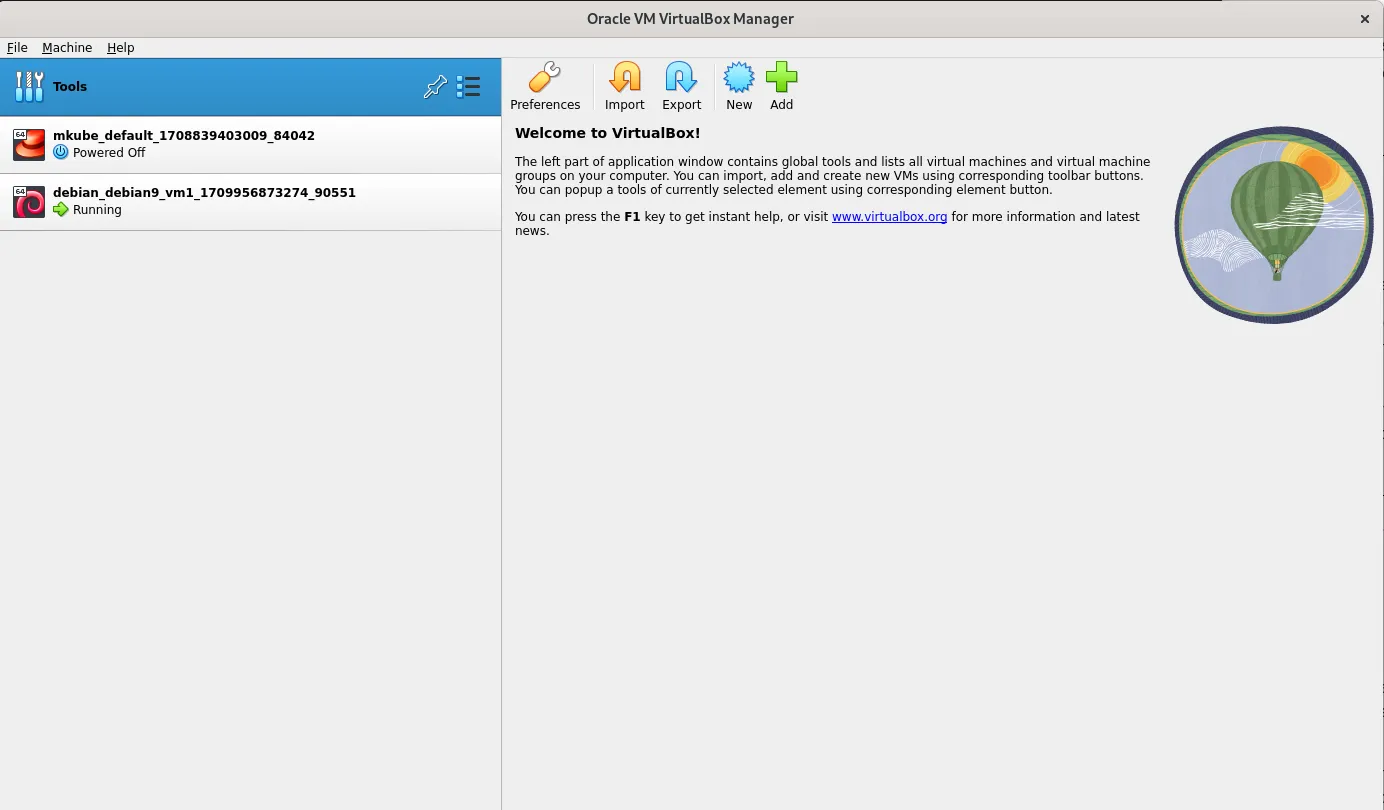
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), on the other hand, is a type 1 hypervisor integrated directly into the Linux kernel. This gives it a performance advantage over Virtualbox, as it can leverage the full power of the host hardware without the additional overhead of running on top of an existing operating system.
KVM is often favored in enterprise environments and data centers where performance and scalability are paramount. It provides support for hardware virtualization extensions like Intel VT-x and AMD-V, allowing for near-native performance when running virtual machines. Additionally, KVM offers advanced features such as live migration, which enables seamless movement of virtual machines between hosts without downtime.
While KVM excels in performance and scalability, it may have a steeper learning curve compared to Virtualbox, especially for users who are not familiar with Linux or command-line interfaces. Setting up and configuring KVM may require more technical expertise, but the payoff is often worth it for those seeking top-notch performance and reliability.
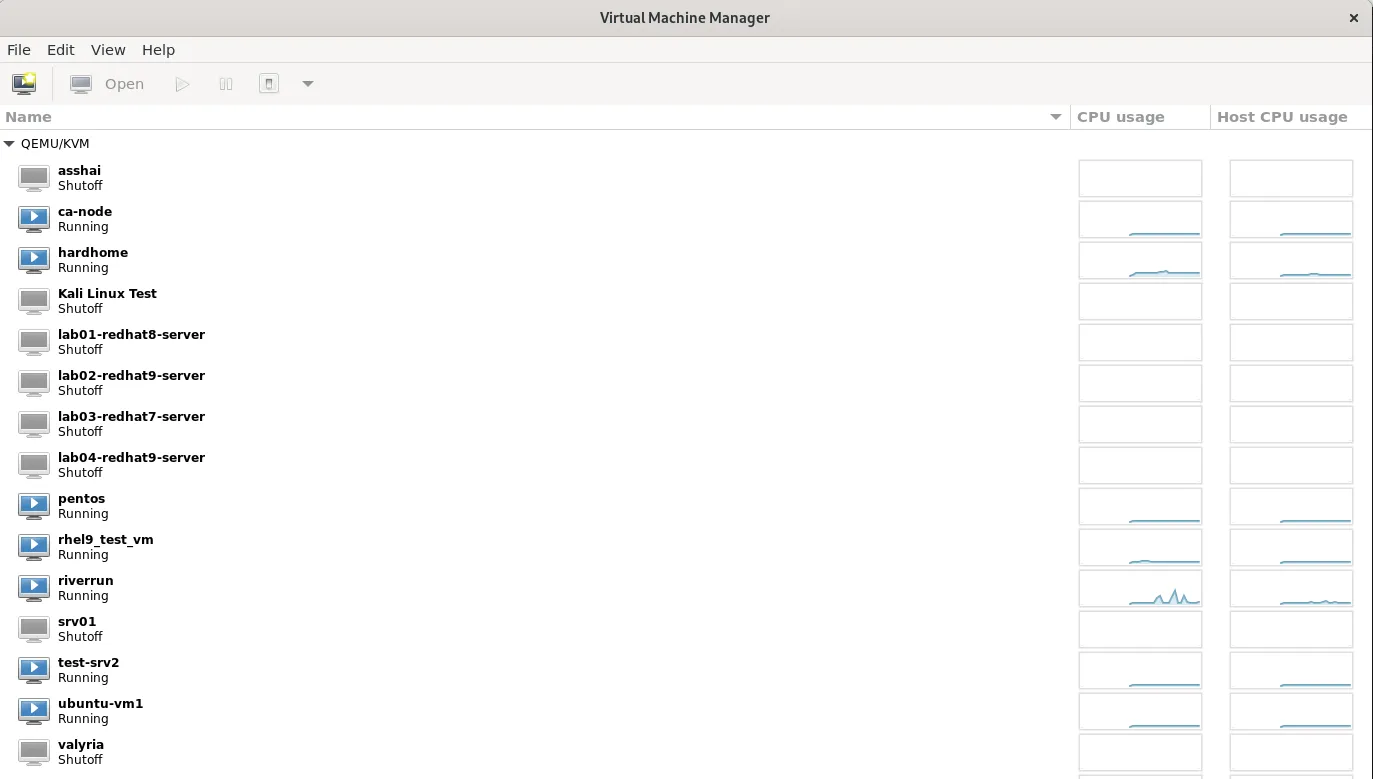
Photo by admingeek from Infotechys
To help you compare Virtualbox and KVM at a glance, here’s a summary of their key differences:
| Feature | Virtualbox | KVM |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Type 2 Hypervisor | Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-metal) |
| Performance | Moderate | High |
| Guest OS Support | Extensive | Limited to Linux and Windows |
| Ease of Use | Beginner-friendly | Requires more technical expertise |
| Features | Snapshotting, Shared Folders, Seamless Mode | Live Migration, Hardware Virtualization Extensions |
So, which virtualization solution is right for you? It ultimately depends on your specific needs and priorities.
If you’re a beginner or need a user-friendly solution with broad guest OS support, Virtualbox may be the way to go. Its intuitive interface and extensive feature set make it a solid choice for casual users and developers alike.
On the other hand, if you require top-notch performance and scalability for enterprise workloads, KVM shines as a powerhouse hypervisor. While it may have a steeper learning curve, the performance benefits and advanced features make it worth considering for more demanding use cases.
Both Virtualbox and KVM are formidable virtualization platforms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the differences between the two, you can make an informed decision that best suits your requirements. Whether you prioritize ease of use or performance, there’s a virtualization solution out there for you.
Did you find this article useful? Your feedback is invaluable to us! Please feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Related Posts

In this article, we will compare Btrfs and LVM and determine which filesystem is better. This should be an interesting read…why you ask? Table of
In this blog post, we’ll explore the 10 major differences between Ubuntu 20.04 and its latest iteration, Ubuntu 22.04, shedding light on the advancements that await
